Product
Pneumatic/electric single-seat regulating valve
Pneumatic/electric single-seated regulating valves use a top-guided structure, featuring a compact structure, small size, light weight, and sensitive operation. The flow path is S-shaped, resulting in low pressure drop, high flow capacity, accurate flow characteristics, and easy maintenance. Equipped with a multi-spring actuator or electric actuator, it can be used in harsh working conditions. It is especially suitable for applications with small allowable leakage and small pressure difference across the valve. This series of products includes standard, heat dissipation, low temperature, regulating and shut-off, bellows sealed, and jacketed insulated types. Nominal pressure ratings are PN(MPa) 1.6, 2.5, 4.0, 6.4, 10.0 (150lb, 300lb, 600lb); valve body diameter range DN(mm) 20~400 (3/4”~16”); applicable fluid temperature range -196~+560℃ in various grades; leakage standards include Class I, Class V, Class V; flow characteristics include linear and equal percentage. A wide variety of specifications are available.
Keyword:
- Product Description
-
Pneumatic/electric single-seated regulating valves adopt a top-guided structure, featuring compact structure, small size, light weight, and sensitive action. The flow path is S-shaped streamline, with low pressure drop loss, large flow capacity, accurate flow characteristics, and easy maintenance. Equipped with multi-spring actuators or electric actuators, it can be used in harsh working conditions. It is especially suitable for occasions with small allowable leakage and small pressure difference before and after the valve. This series of products has various types, including standard type, heat dissipation type, low temperature type, regulating and cut-off type, bellows sealed type, and jacketed insulation type. The nominal pressure rating of the product is PN(MPa) 1.6, 2.5, 4.0, 6.4, 10.0 (150lb, 300lb, 600lb); the valve body diameter range is DN(mm) 20~400 (3/4”~16”): applicable fluid temperature is -196~+560℃ in various grades: leakage standards include Class I, Class V, Class V; flow characteristics include linear and equal percentage. A variety of varieties and specifications are available.
Pneumatic:
The positioner receives standard current signals or computer signals, converts them into valve position setpoints, and the linear displacement of the actuator is converted into angular displacement through a connecting device and measured by a position sensor, which is fed back to the microprocessor.
The microprocessor compares the actual valve position feedback value with the set value. After detecting a deviation, it outputs a pulse width modulation instruction (PWVM) to the piezoelectric valve according to the magnitude and direction of the deviation. The piezoelectric valve adjusts the air intake or exhaust volume of the diaphragm head according to the control instruction.
Electric:
The standard current signal or computer signal is converted by A/D conversion and then enters the intelligent signal acquisition and control unit of the intelligent electric actuator. The signal acquisition and control unit constantly monitors the input signal and position feedback signal. When the two signals are unbalanced, according to the magnitude and direction of the deviation
A pulse width modulation instruction (PWM) is output to the bidirectional thyristor, causing it to conduct and drive the motor to rotate in the direction of reducing the deviation, thereby driving the speed reduction mechanism and changing the valve opening.
Control Mode
The control mode uses PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) drive;
Full speed state: When the control deviation is large, a continuous signal is output:
Medium speed state: When the deviation is not large, a pulse signal is output:
Slow fine-tuning: When the deviation is very small, a smaller pulse signal is output.
Maintain positioning: When the deviation is small enough to be within the valve adjustment accuracy range, no control instruction is output.
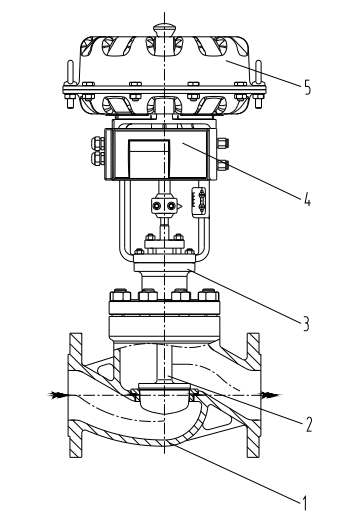
1. Valve body 2. Valve stem 3. Valve cover 4. Positioner 5. Actuator
This series of regulating valves adopts a modular design and can be used with various accessories with different configurations.
Type
Operating temperature -20~+200℃, leakage grade
Heat dissipation type: The valve cover is equipped with a heat sink, which can be used in occasions with a medium temperature of -60~+450℃ (Figure 2)Regulating and cut-off type: The soft-sealed structure valve core reaches the Class V leakage standard (Figure 3)
Bellows sealed type: Completely seals the up and down movement of the valve stem, preventing fluid leakage (Figure 4);
Low temperature type: Using a long neck valve cover and bellows seal, it can be used at -196℃ (Figure 5);
Jacketed insulation type: Used in occasions where fluid cooling easily causes crystallization and clogging. (Figure 6):
PTFE-lined single-seated valve: The parts in contact with the fluid are lined with F46 packing, and the filling parts use polytetrafluoroethylene bellows seals, especially suitable for automatic control of strong corrosive media (Figure 7):
The valve core and valve seat are overlay welded with Stellite alloy, suitable for high temperature, cryogenic and other harsh working conditions.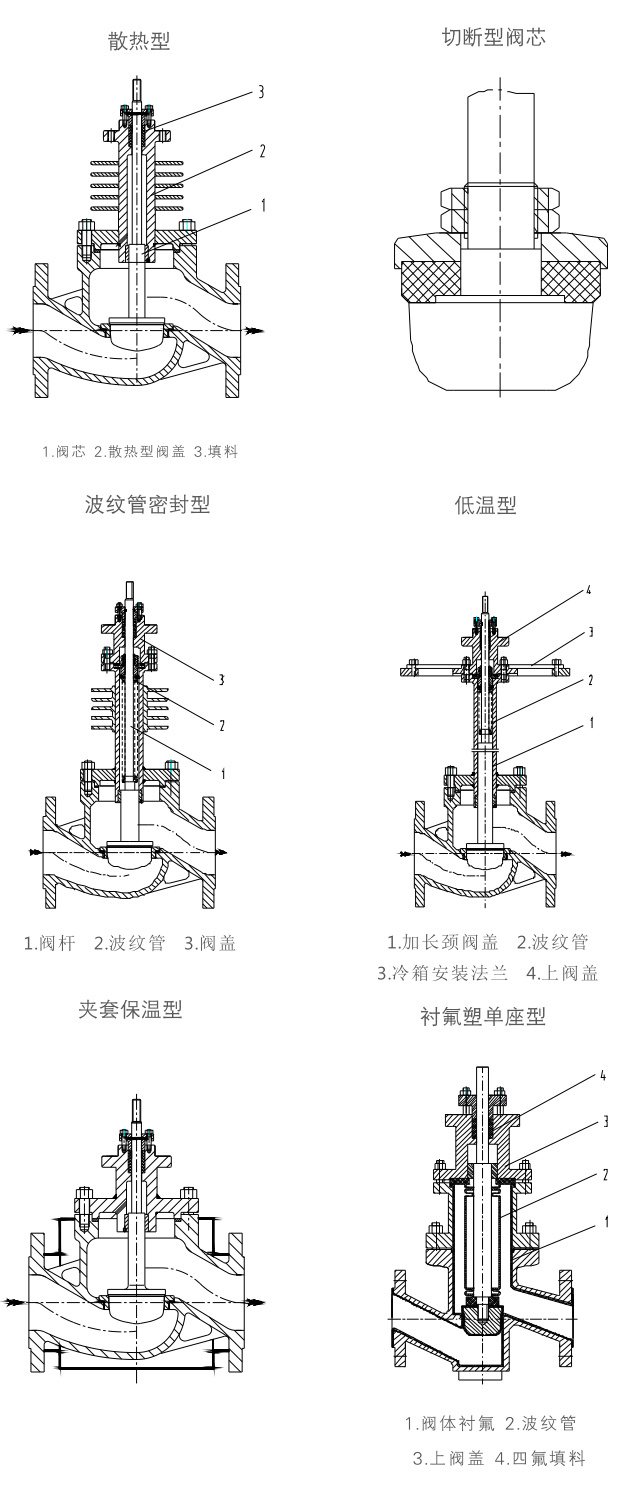
Keyword:
Benefiting from all the advantages of the 1ZQ actuator, the IZQ+VE features a linear output transmission system, with adjustable thrust output up to 100KN
IZQ-Multi-turn Actuator Model 18-40
Advanced intelligent non-invasive electric valve actuators, offering multi-turn, partial-turn, and linear stroke options.
Part of the IZQ+BW rotary actuator
The IZQ+BW actuator is based on the IZQ multi-turn actuator with a secondary deceleration stage, enabling 90° opening and closing of large-diameter, high-torque butterfly valves, ball valves, etc., with a torque range of 1000Nm~63000Nm
I want to consult
*Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication open. We will contact you as soon as possible.




