Product
Electric/pneumatic diaphragm three-way regulating valve
The pneumatic/electric three-way regulating valve uses a cylindrical thin-walled window-shaped valve core guide, unlike the bushing guide of a plunger-type valve core. Equipped with a multi-spring actuator, the valve body has a four-way structure, namely one inlet and two outlets (split flow type), and two inlets and one outlet (merged flow type), thus achieving fluid mixing for heating or cooling, or unequal fluid splitting, to meet the requirements of different operating conditions. This valve has the advantages of compact structure, light weight, sensitive action, small pressure drop loss, large valve capacity, and easy maintenance. <br/> This series of products includes standard, heat dissipation, and bellows sealed types. The nominal pressure ratings are PN(MPa) 1.6, 2.5, 4.0, 6.4, 10.0 (150lb, 300lb, 600lb); the valve body diameter range is DN(mm) 25~250 (1”~10”); applicable fluid temperature ranges from -40~+450℃; leakage grade: Ⅳ; flow characteristics include linear and equal percentage. A variety of types and specifications are available.
Keyword:
- Product Description
-
The pneumatic/electric three-way regulating valve uses a cylindrical thin-walled window-shaped valve core guide, unlike the bushing guide of a plunger-shaped valve core. It is equipped with a multi-spring actuator, and the valve body has a four-way structure, namely one inlet and two outlets (split flow type), and two inlets and one outlet (merged flow type), thus achieving fluid mixing for heating or cooling, or unequal flow splitting, to meet the requirements of different operating conditions. This valve has the advantages of compact structure, light weight, sensitive action, small pressure drop loss, large valve capacity, and easy maintenance.
This series of products includes standard types, heat dissipation types, bellows sealed types, and other types. The nominal pressure ratings of the products are PN (MPa) 1.6, 2.5, 4.0, 6.4, 10.0 (150lb, 300lb, 600lb); the valve body diameter range is DN (mm) 25~250 (1”~10”); applicable fluid temperature range is -40~+450℃; leakage grade: Ⅳ; flow characteristics include linear and equal percentage. A variety of varieties and specifications are available.
Working principle:
Pneumatic
The positioner receives a standard current signal or computer signal, converts it into a valve position setpoint, and the linear displacement of the actuator is converted into angular displacement through a connecting device and measured by a position sensor, which is fed back to the microprocessor. The microprocessor compares the actual valve position feedback value with the setpoint, and when a deviation is detected, it outputs a pulse width modulation (PWM) instruction to the piezoelectric valve according to the magnitude and direction of the deviation. The piezoelectric valve adjusts the air intake or exhaust volume of the diaphragm head according to the control instruction.
Electric
The standard current signal or computer signal is converted to an A/D signal and then enters the intelligent signal acquisition and control unit of the intelligent electric actuator. The signal acquisition and control unit constantly monitors the input signal and position feedback signal. When the two signals are unbalanced, it outputs a pulse width modulation (PWM) instruction to the bidirectional thyristor according to the magnitude and direction of the deviation, causing it to conduct and drive the motor to rotate in the direction of reducing the deviation, thereby driving the speed reduction mechanism and changing the valve opening.
Control mode:
The control mode uses PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) drive;
Full speed state: When the control deviation is large, a continuous signal is output;
Medium speed state: When the deviation is small, a pulse signal is output;
Slow fine-tuning: When the deviation is very small, a smaller pulse signal is output.
Maintain positioning: When the deviation is small enough to be within the valve adjustment accuracy range, no control instruction is output.
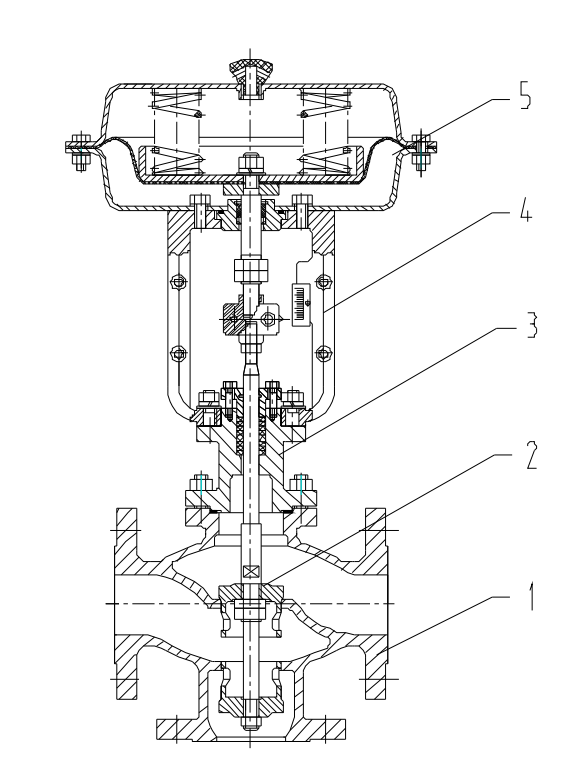 1. Valve body 2. Valve core 3. Valve cover 4. Bracket 5. Actuator
1. Valve body 2. Valve core 3. Valve cover 4. Bracket 5. Actuator This series of regulating valves adopts a modular design and can be used with various combinations and accessories.
Type:Standard type: Operating temperature -20~+250℃, leakage grade IV;
Heat dissipation type: A heat sink is added to the valve cover, which can be used in occasions with a medium temperature of -60~+450℃:
Bellows sealed type: Completely seals the up and down movement of the valve stem, preventing fluid leakage.
Note: Bellows sealed type and heat dissipation type structures are both suitable for pneumatic three-way merged and split flow types.
Keyword:
Benefiting from all the advantages of the 1ZQ actuator, the IZQ+VE features a linear output transmission system, with adjustable thrust output up to 100KN
IZQ-Multi-turn Actuator Model 18-40
Advanced intelligent non-invasive electric valve actuators, offering multi-turn, partial-turn, and linear stroke options.
Part of the IZQ+BW rotary actuator
The IZQ+BW actuator is based on the IZQ multi-turn actuator with a secondary deceleration stage, enabling 90° opening and closing of large-diameter, high-torque butterfly valves, ball valves, etc., with a torque range of 1000Nm~63000Nm
I want to consult
*Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication open. We will contact you as soon as possible.




